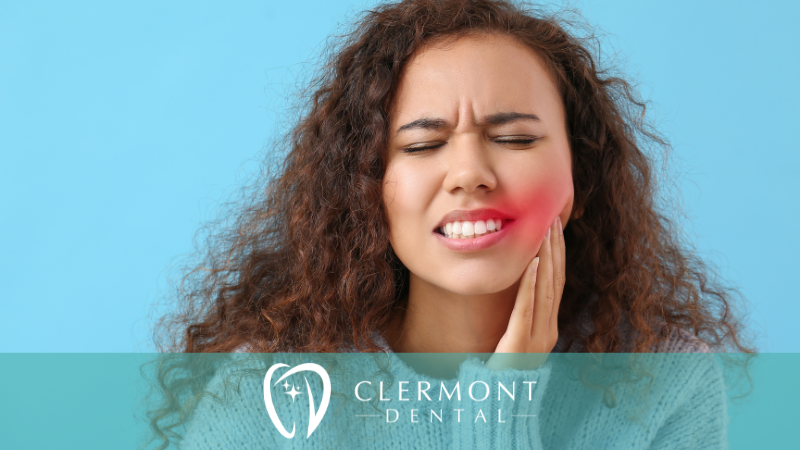
There’s nothing quite as nagging and uncomfortable as a sudden toothache. One moment you’re enjoying a delicious meal or going about your day, and the next, a sharp pain shoots through your tooth, bringing everything to a screeching halt. Toothaches can be disruptive and even debilitating at times, impacting our overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explore some potential reasons why people experience toothaches and what you can do about them.
1. Tooth Decay: The Culprit Behind Most Toothaches
Tooth decay is by far the most common cause of toothaches. When bacteria in our mouth feed on the sugars and starches we consume, they produce acids that erode tooth enamel. Over time, this erosion creates cavities, exposing the sensitive inner layers of the tooth. When these layers become irritated or infected, they can cause intense tooth pain.
To prevent tooth decay and the resulting toothaches, maintaining good oral hygiene practices is crucial. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss regularly, and visit your dentist for check-ups and cleanings.
2. Dental Abscess: A Serious Infection
A dental abscess is another potential cause of toothaches. It occurs when a bacterial infection forms a pocket of pus within the tooth or gums. Abscesses are typically accompanied by throbbing pain and swelling. If left untreated, they can lead to more severe complications and possibly spread to other parts of the body.
If you suspect a dental abscess, it’s essential to seek immediate dental care. Your dentist will evaluate the abscess and prescribe appropriate antibiotics to fight the infection and relieve the pain.
3. Gum Disease: A Stealthy Saboteur
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is often caused by poor oral hygiene, leading to the accumulation of bacteria-laden plaque and tartar. As gum disease progresses, it can cause gum inflammation, receding gums, and ultimately tooth loss.
In the early stages of gum disease, toothaches might not be the primary symptom. However, as the infection worsens, tooth sensitivity and pain can occur. Regular dental exams and cleanings, along with thorough oral hygiene practices, can help prevent and manage gum disease.
4. Tooth Fracture: When the Structure Crumbles
A cracked or fractured tooth can be a painful experience. Biting into hard food, suffering a traumatic injury, or even grinding your teeth can result in tooth fractures. Depending on the severity of the fracture, you may experience intermittent tooth pain or constant discomfort.
Treatment options for tooth fractures vary based on the location and extent of the damage. Your dentist may recommend dental bonding, a crown, or, in severe cases, extraction.
5. Tooth Sensitivity: Nerves on High Alert
Tooth sensitivity is a common problem that can cause fleeting pain or discomfort when exposed to certain stimuli like hot or cold temperatures, sweet or acidic foods, or even cold air. It occurs when the protective layer of tooth enamel wears thin, exposing the sensitive dentin underneath. This dentin contains tiny channels that connect to the nerve endings, leading to sensitivity and occasional toothaches.
Using toothpaste designed specifically for sensitive teeth and adopting gentle brushing techniques can help manage tooth sensitivity. If the sensitivity persists or worsens, consult your dentist for further evaluation.
6. Sinus Infection: The Surprising Connection
Believe it or not, a sinus infection can sometimes cause tooth pain. When the sinuses become inflamed and congested, the increased pressure can radiate pain to the upper teeth. This type of toothache is often accompanied by other symptoms such as facial pressure, nasal congestion, and post-nasal drip.
Usually, treating the sinus infection with appropriate medication will alleviate the associated tooth pain. Consult with your healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and appropriate treatment options.
What to Do When Tooth Pain Strikes
Regardless of the cause, experiencing a toothache is a sign that something is not right. While over-the-counter pain relievers may temporarily alleviate the discomfort, it is essential to visit your dentist as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
In the meantime, you can rinse your mouth with warm saltwater, apply a cold compress to the affected area, use topical numbing gels, and avoid chewing on that side of your mouth. However, these are temporary measures, and professional dental care is crucial to address the underlying cause of the pain.
Remember, prevention is the best medicine. By maintaining good oral hygiene, visiting your dentist regularly, and addressing dental issues promptly, you can minimize the chances of experiencing toothaches and keep your smile healthy and pain-free.