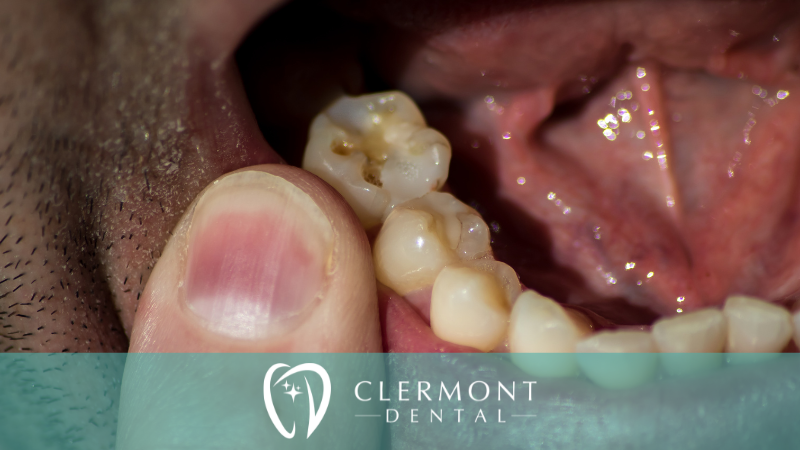
Molar teeth are an essential part of our dental structure, located at the back of the mouth. They play a crucial role in chewing food and facilitating proper digestion. However, many people experience pain in their molar teeth at some point in their lives. Experiencing pain in your molar teeth can be a distressing experience. While occasional sensitivity or discomfort may be normal, persistent or severe molar tooth pain is not.
Understanding the causes of molar tooth pain, such as dental issues, sensitivity, gum disease, and bruxism, is key to finding effective relief and protecting your oral health.
What are Molar Teeth?
Molar teeth are large, flat teeth located at the back of the mouth, designed for grinding and chewing food. Adults typically have twelve molars, divided into four quadrants – upper right, upper left, lower right, and lower left. These teeth have multiple cusps, or raised points, that aid in the grinding of food.
Causes of Molar Tooth Pain
- Tooth Decay: A common culprit behind molar tooth pain. Tooth decay, cavities, infections, and gum disease can all lead to discomfort and pain. The intricate anatomy of molars and their position in the mouth make them susceptible to bacterial growth and decay, resulting in pain and sensitivity.
- Sensitivity (Hot/Cold): Molar tooth pain can also result from tooth sensitivity. Excessive enamel wear, gum recession, or exposed tooth roots can make the nerves in your teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli. This sensitivity can cause sharp, fleeting pain or a lingering ache in your molars.
- Gum Disease: Another potential cause of molar tooth pain is gum disease, also known as periodontitis. This inflammatory condition affects the gums, causing swelling, tenderness, and pain in the affected area. As the disease progresses, it can lead to tooth mobility and discomfort.
- Bruxism: Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding or clenching, can put excessive pressure on the molars, leading to pain over time. This habit often occurs during sleep or in response to stress. The constant grinding can wear down the enamel, causing sensitivity and pain.
Bruxism: A Major Culprit
Bruxism deserves special mention due to its prevalence and impact on molar tooth pain. As mentioned earlier, bruxism is the habit of grinding or clenching the teeth, often unconsciously. When it comes to molars, the constant pressure and grinding can result in cracked teeth, tooth sensitivity, generalized pain in the jaw, and headaches. Identifying and addressing bruxism is crucial to alleviating molar tooth pain and preserving dental health.
Protecting Your Molar Teeth
Fortunately, several effective ways exist to protect your molars from pain and mitigate existing discomfort. Consider the following practices:
- Regular Dental Care: Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice daily and flossing, is vital for healthy molars. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings help detect and prevent dental issues that can lead to molar pain.
- Addressing Bruxism: Consult with your dentist if you suspect you suffer from Bruxism. They or Dr.Safavi may recommend a custom-made mouthguard to be worn at night, which helps reduce the impact of grinding on the molars. Stress reduction techniques such as yoga or meditation may also help minimize bruxism-related pain.
- Managing Sensitivity: If you experience tooth sensitivity in your molars, try using desensitizing toothpaste or rinse to alleviate the discomfort. Avoiding extremely hot or cold foods and beverages can also help minimize sensitivity.
- Treating Gum Disease: If you suspect gum disease is the cause of your molar tooth pain, consult with your dentist or periodontist for appropriate treatment. This may involve deep cleaning, gum surgery, or other procedures to control the infection and reduce pain.
- Wisdom Teeth Management: If you experience pain due to impacted wisdom teeth, your dentist may recommend their extraction. This proactive approach can alleviate pain and prevent future complications.
- Dietary Considerations: Be mindful of what you eat. Avoid excessively hard or sticky foods that might exert excessive force on your molars and potentially cause tooth fractures. Opt for a balanced diet, rich in calcium and vitamin D, which aid in maintaining overall oral health.
- Treat Dental Issues Promptly: Regular dental check-ups allow for the early detection and treatment of cavities, tooth decay, and gum disease. Promptly addressing these issues prevents the development of more severe problems and molar pain.
Conclusion
Pain in your molar teeth is not normal and should not be ignored. Understanding the causes of molar tooth pain, such as dental issues, sensitivity, gum disease, and bruxism, is vital in seeking appropriate treatment and relief. By maintaining good oral hygiene, addressing bruxism, managing sensitivity and gum disease, and seeking professional dental care promptly, you can protect your molars and enjoy a pain-free smile for years to come. Remember, if you experience persistent or severe molar tooth pain, consult with your dentist for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.